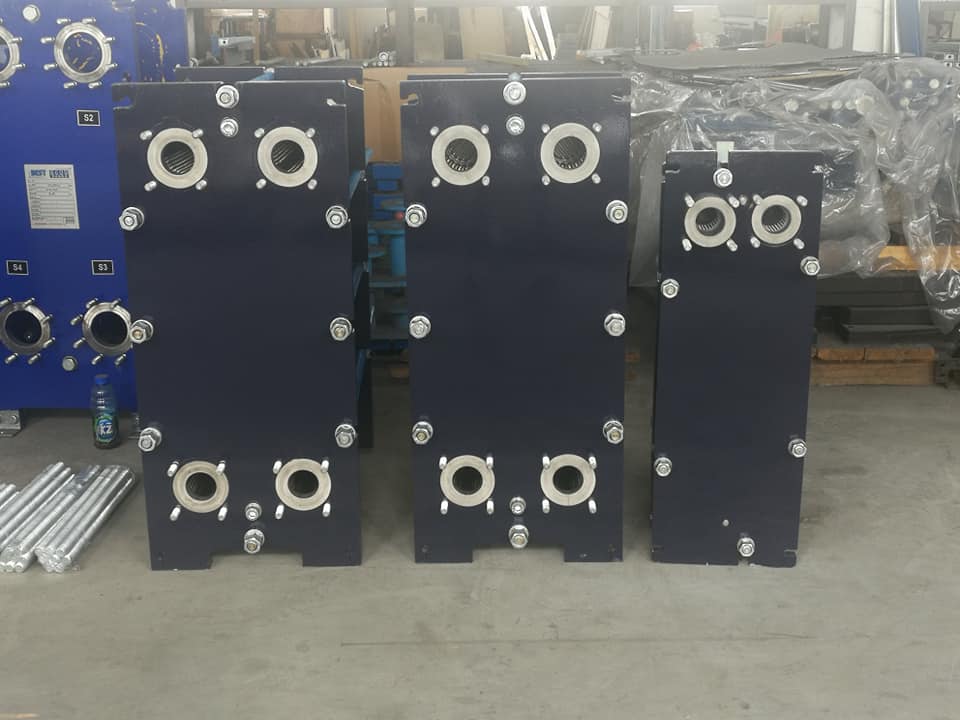
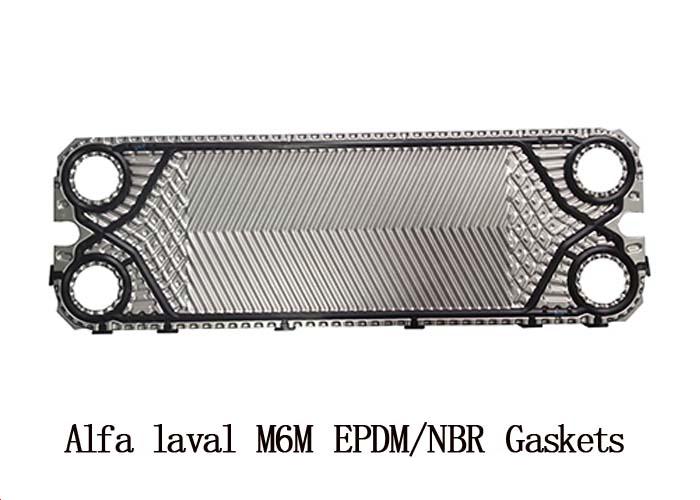
Product Introduction
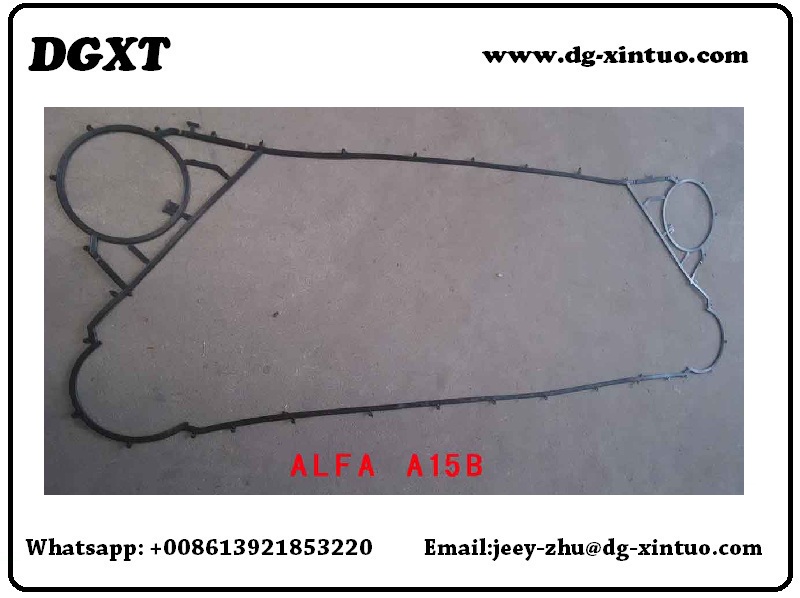
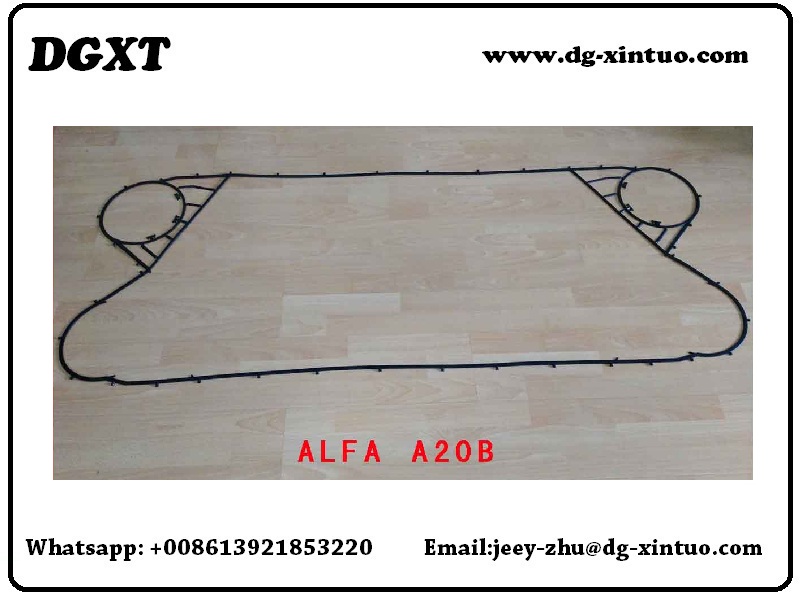
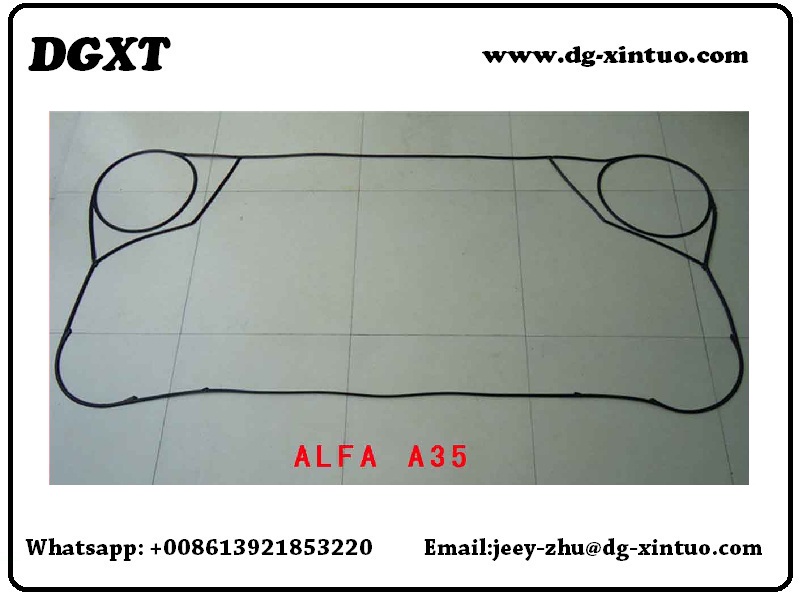
Alfa Laval A Series Original Gaskets & Plates For Alfa Laval Plate Heat Exchanger
Alfa Laval Model List as below.
| A3 | A10 | A10-B | A15 | A15-B | A20 | A20-B |
|
|
...... |
|
|
|
|
|
Gaskets Information:
Gasket - materials
• The choice of rubber material depends on
– Fluids - chemical attack or not
– The combination of temperature and pressure
• Rubber materials change properties due to
– Time - the rubber relaxes
– Temperature - the rubber deteriorates
– Hardening by attack of oxidising agents (e.g., oxygen in air)
– Swelling or softening by absorption of chemicals in the fluids
• Common gasket types
– Nitrile– EPDM– FKM
• Nitrile
– Inexpensive standard material up to 130°C
• NBR P (performance) up to 130°C
• NBR B (base) inexpensive for lower temperatures
– Application related NBR qualities
• NBR HTF - food grade for high temperatures
• NBR LT - for low temperature in refrigeration applications
• H NBR (hydrogenated) for duties where normal NBR swells and for higher temperatures, more expensive
• EDPM
– Standard material up to 160 °C
– Standard EPDM qualities
• EPDM for glued gaskets (“Crushing resistant”)
• EPDMC for clip-on gaskets at high temperature
• EPDMCT as above but for thin gaskets in models with low
pressing depth (1.5-3 mm)
– Application related EPDM qualities
• EPDMF - food grade
• EPDM AL for increased pressure resistance in certain chemical
duties where normal EPDM swells
• FKM, Fluorocarbon rubber
– Often called Viton (DuPont trade name)
– Used for aggressive chemical compounds
• Sulphuric acid
• Aromatic organic compounds
• Chlorinated organic compounds
– Two different qualities used
• FKM G
• FKM S
• Other types are Neopren, Hypalon, Chloroprene, etc.
Gaskets- sealing lifetime
Product
• Gasket material
• Fastening
– Glue or glue-free
– Type of glue
• Gasket geometry
• Gasket groove
• Alignment of plate pack
Duty
• Operating temperature
• Operating pressure
• Media
• Type of operation
continuous / cyclic
• Cleaning methods &
chemicals
• Opening frequency
• Maximum temperature in CAS and product manual,
for example,
– NBR up to 130ºC
– EPDM up to 160ºC
⇒ Gives about 1 year lifetime
When no chemical attack takes place
• Rule of thumb:
– 10ºC lower than max temperature
⇒ 2 years lifetime
– 10ºC above the max temperature
⇒ 6 months lifetime
• Temperature
– Considered in CAS
– Selects a gasket which gives minimum 1 year lifetime
at the design temperature
– Manual check if other gasket is needed to get longer lifetime
• When aggressive fluids are present
– Gasket Selection Guide programme
– Ask the customer
– Contact the Market Segment
– Testing with small test-gaskets in the customers process
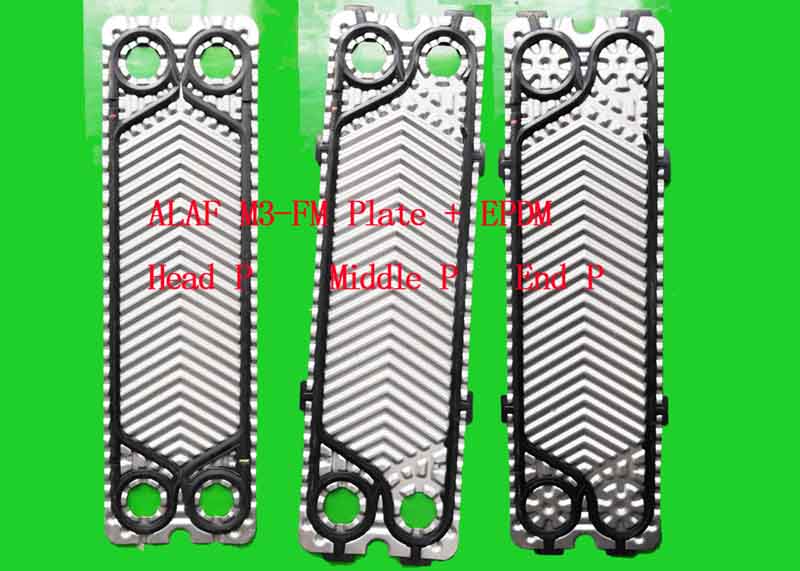
Plate Information:
Plate - materials
• Standard materials and thicknesses
– AISI 304 (stainless steel)
• Usually 0.4 or 0.5 mm thickness
• Cheapest possible solution
– AISI 316 (stainless steel)
• Always 0.5 and 0.6 mm
• Some with thicker plates (high-pressure applications)
– 254 SMO (high-alloy stainless steel)
• Usually in 0.6 mm to allow stock-keeping
– Titanium
• Always 0.5 and 0.6 mm
• Some with thicker plates (high-pressure applications)
• Some PHEs with 0.4 mm (low-pressure applications)
– Alloy C-276 (Nickel alloy)
• Usually in 0.6 mm to allow stock-keeping
• Standard materials and typical uses
– AISI 304
• Typically in clean water-water duties
• Example, up to 50 ppm chlorides at 50°C
– AISI 316
• Typically in water-water duties
• Example, up to 250 ppm chlorides at 50°C
– 254 SMO (high-alloy stainless steel)
• Many uses including high-chloride water-water duties
• Example, up to 6000 ppm chlorides at 50°C
– Titanium
• Most frequent use is for sea water (3.5% chlorides)
• Example, up to 130°C in sea water
– Alloy C-276 (Nickel alloy)
• Most frequent use is for concentrated sulphuric acid up to 90°C
• Common exotic materials
– Not always on stock
– Check with Supply Unit before quoting and confirm before order
– 904L is an alternative to 254 SMO in some applications
– Nickel 200/201 is mainly for sodium hydroxide production
– Titanium Palladium
• For sea water at high temperature (>130°C)
• For high concentrated chloride brines at high temperature
– Alloy G-30 is used in the sulphuric acid application (scrubber)
– Alloy D-205 is exclusively for concentrated sulphuric acid >90°C
• Many more are used less frequently on a case-by-case basis
How to know which plate material to use?
– Application Manual
– Contact the Market Segment
– Ask the customer
– Testing with small test-pieces in the customers process